How to Write Floor Brackets (⌊ ⌋) in LaTeX
In LaTeX, you can write floor brackets using the \lfloor and \rfloor commands.
The following examples show how to write floor brackets in LaTeX.
How to Write Floor Brackets in Text
For text, we can use the standard keyboard characters, but for proper mathematical formatting, we can use the \lfloor and \rfloor commands.
Example: Floor Brackets in Text
Suppose we want to write floor brackets in the text.
We can use the following LaTeX code to do so:
\documentclass{article}
\begin{document}
This is an example of using floor brackets \(\lfloor x \rfloor\) in a sentence.
\end{document}
Output: 👇️
This is an example of using floor brackets ⌊x⌋ in a sentence.
In this example, we use the floor brackets to enclose a variable in the text.
How to Write Floor Brackets in Mathematical Expressions
For mathematical expressions, we should use the \lfloor and \rfloor commands to ensure proper formatting.
Example: Floor Brackets in Mathematical Expressions
Suppose we would like to write mathematical expressions that contain floor brackets.
We can use the following LaTeX code to do so:
\documentclass{article}
\begin{document}
An inline mathematical expression: \( \lfloor a + b \rfloor \).
A displayed mathematical expression:
\[
\left\lfloor \frac{a}{b} \right\rfloor + \left\lfloor \frac{c}{d} \right\rfloor
\]
\end{document}
Output: 👇️
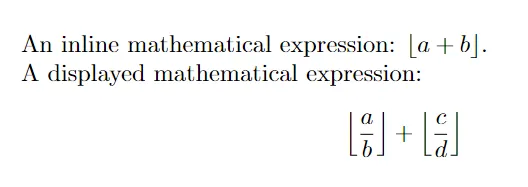
In this example, we use the \lfloor and \rfloor commands to enclose elements in a floor function. The \left\lfloor and \right\rfloor commands are used to adjust the size of the floor brackets to fit the enclosed fractions.
Conclusion
We can use the \lfloor and \rfloor commands for both text and mathematical expressions.
For larger expressions, the \left\lfloor and \right\rfloor commands help in adjusting the size of the floor brackets automatically.