How to Write the Not Precede or Equal Symbol (⋠) in LaTeX
In LaTeX, you can write the not precede or equal symbol (⋠) using the \npreceq command. This command is part of the amssymb package, so you need to include this package in your LaTeX document.
The following examples show how to write the not precede or equal symbol in LaTeX.
How to Write the Not Precede or Equal Symbol in Text
We can use the \npreceq command to write the not precede or equal symbol in LaTeX document for text.
Suppose we want to write the not precede or equal symbol in the text.
We can use the following LaTeX code to do so:
\documentclass{article}
\usepackage{amssymb}
\begin{document}
This is an example of using the not precede or equal symbol \( a \npreceq b \) in a sentence.
\end{document}
Output: 👇️
This is an example of using the not precede or equal symbol a ⋠ b in a sentence.
In this example, we use the \npreceq command to display the not precede or equal symbol in the text.
How to Write the Not Precede or Equal Symbol in Mathematical Expressions
For mathematical expressions, we can use the \npreceq command to ensure proper formatting.
Suppose we would like to write mathematical expressions that contain the not precede or equal symbol.
We can use the following LaTeX code to do so:
\documentclass{article}
\usepackage{amssymb}
\begin{document}
An inline mathematical expression: \( a \npreceq b \).
A displayed mathematical expression:
\[
a \npreceq b
\]
\end{document}
Output: 👇️
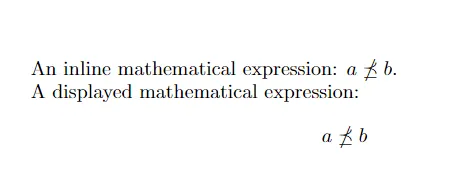
In this example, we use the \npreceq command to denote the not precede or equal symbol in both inline and displayed mathematical expressions.
Conclusion
We can use the \npreceq command from the amssymb package for both text and mathematical expressions. This ensures that the not precede or equal symbol is properly formatted and displayed in your LaTeX document.